
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry: Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras for the Selective Degradation of Mcl-1/Bcl-2 Derived from Nonselective Target Binding Ligands
Authors: Ziqian Wang, Nianzhe He, Zongwei Guo, Cuili Niu, Ting Song, Yafei Guo, Keke Cao, Anhui Wang, Junjie Zhu, Xiaodong Zhang, and Zhichao Zhang*
Abstract
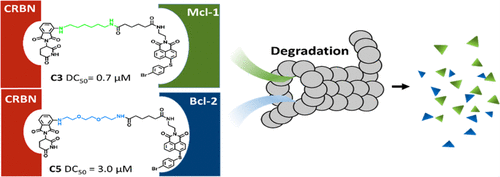
Proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) recruits an E3 ligase to a target protein to induce its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. We reported success in the development of two PROTACs (C3 and C5) that potently and selectively induce the degradation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 (DC50 = 0.7 and 3.0 μM), respectively, by introducing the E3 ligase cereblon-binding ligand pomalidomide to Mcl-1/Bcl-2 dual inhibitors S1-6 and Nap-1 with micromolar-range affinity. C3-induced Mcl-1 ubiquitination translated into much more lethality in Mcl-1-dependent H23 cells than the most potent Mcl-1 occupancy-based inhibitor A-1210477 with nanomolar-range affinity. Moreover, structure–activity relationship analysis and molecular dynamic simulations discovered the structural basis for turning nonselective or promiscuous Bcl-2 family ligands into selective PROTACs. C3 and C5 exhibited reversible depletion in living cells, which provides a new potent toolkit for gain-of-function studies to probe the dynamic roles of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 in apoptosis networks.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00919