
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl (COVER): Deactivation of Mcl-1 by Dual-Function Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Bcl-2 Homology 3 Domain and Facilitating Mcl-1 Ubiquitination
Authors: Dr. Ting Song, Ziqian Wang, Dr. Fangling Ji, Dr. Yingang Feng, Yudan Fan, Gaobo Chai, Dr. Xiangqian Li, Zhiqiang Li, Dr. Zhichao Zhang

Graphical Abstract
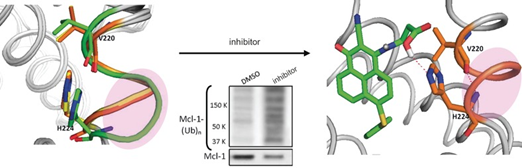
Switched: By using NMR methods and structure–activity relationship studies it was shown that a small-molecule inhibitor could induce the flexible QRN motif to form a helical conformation through interaction with His224, by which it facilitates Mcl-1 ubiquitination in living cells. The inhibitor demonstrates that Mcl-1 ubiquitination can be chemically exploited to effectively facilitate its deactivation, thus identifying an avenue for pharmacological intervention in Mcl-1 signaling.
Abstract
By means of limited proteolysis assay, three-dimensional NMR, X-ray crystallography and alanine mutations, a dynamic region at the Q221R222N223 motif in the Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain of Mcl-1 has been identified as a conformational switch which controls Mcl-1 ubiquitination. NoxaBH3 binding biases the QRN motif toward a helical conformation, thus leading to an enhanced in vitro ubiquitination of Mcl-1. In contrast, BimBH3 binding biases the QRN motif toward a nonhelical conformation, thus leading to the inhibition of ubiquitination. A dual function Mcl-1 inhibitor, which locates at the BH3 domain of Mcl-1 and forms hydrogen bond with His224 to drive a helical QRN conformation, so that it not only interferes with the pro-apoptotic partners, but also facilitates Mcl-1 ubiquitination in living cells, is described. As a result, this inhibitor manifests a more effective apoptosis induction in Mcl-1-dependent cancer cells than other inhibitors exhibiting a similar binding affinity with it.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201606543